The term cloud has been used as a metaphor for the Internet. The cloud has been used in the networks diagram to represent the transport of data across carrier backbones to an endpoint on the other side of the cloud. As the cloud has no borders and is global in nature same way the Internet has made the world a smaller place in which everyone can reach anyone anytime and resources available can be shared among all those who need them at any time and at any place. A cloud is more than a collection of computer resources because a cloud provides a mechanism to manage those resources. So cloud can be thought of as a pool of virtualized computer resources. A cloud can:
- Host a variety of different workloads, including batch-style back-end jobs and interactive, user-facing applications .
- Allow workloads to be deployed and scaled-out quickly through the rapid provisioning of virtual machines or physical machines.
- Support redundant, self-recovering, highly scalable programming models that allow workloads to recover from many unavoidable hardware/software failures.
- Monitor resource use in real time to enable rebalancing of allocations when needed.
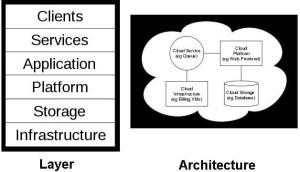
Cloud Computing is a computing that provides an abstraction between the resources and its structure like where they are stored,in which network are they and where the servers are located thus providing convenient ,on –demand shared computing resources without much efforts and cost having interaction with the service providers. Cloud computing also describes applications that are extended to be accessible through the Internet. These cloud applications use large data centers and powerful servers that host Web applications and Web services. Anyone with a suitable Internet connection and a standard browser can access a cloud application. Cloud computing uses the model of utility computing which means that users will be charged for what services they use and how much rather than being charged for all the services just like the subscription utilities and other public utilities like electricity and telephone, the users are charged for the amount of electricity they consume and the total amount of call time they use.
The cloud computing has two sections front end and back end. Front end is basically the client’s computer and the application that is used to connect to the network to access the cloud resources through cloud computing systems. The common example of one of the cloud computing is the web based mails, the user uses various mail services like Gmail, Yahoo mail for communication and the mails are not stored on client side so client is not to bother about the storage rather they are stored somewhere else on the servers of email providers so the users can access their mails whenever they want. The front end ie interface software required in this case is the web browser. SaaS (Software- a-s a- Service) is a type of cloud computing that delivers applications through a browser to thousands of customers using a multiuser architecture. The focus for SaaS is on the end user as opposed to managed services. For the customer, there are no up-front investment costs in servers or software licensing. For the service provider, with just one product to maintain, costs are relatively low compared to the costs incurred with a conventional hosting model.
Amazon S3 storage service is the example of SaaS designed to use across the Internet. Amazon S3 provides a simple web services interface that can be used to store and retrieve any amount of data, at any time, from anywhere on the web. It gives any developer access to the same highly scalable, reliable, fast, inexpensive data storage infrastructure that Amazon uses to run its own global network of web sites. The service aims to maximize benefits of scale and to pass those benefits on to developers. SaaS is also commonly used for enterprise resource planning and human resource applications. Another example is Google Apps, which provides online access via a web browser to the most common office and business applications used today, all the while keeping the software and user data stored on Google servers. Google App Engine environment includes the following features
- Dynamic web serving, with full support for common web technologies.
- Persistent storage with queries, sorting, and transactions.
- Automatic scaling and load balancing .
- APIs for authenticating users and sending email using Google Accounts.
- A fully featured local development environment that simulates Google App Engine on your computer.
CaaS (Commuincation–as-a-Service)is an outsourced enterprise communications solution. Providers of this type of cloud-based solution (known as CaaS vendors) are responsible for the management of hardware and software required for delivering Voice over IP (VoIP) services, Instant Messaging (IM), and video conferencing capabilities to their customers. This model began its evolutionary process from within the telecommunications (Telco) industry, not unlike how the SaaS model arose from the software delivery services sector. CaaS vendors are responsible for all of the hardware and software management consumed by their user base. CaaS vendors typically offer guaranteed quality of service (QoS) under a service-level agreement (SLA). A CaaS model allows a CaaS providerís business customers to selectivelydeploy communications features and services throughout their company ona pay-as-you-go basis for service(s) used. CaaS is designed on a utility-like pricing model that provides users with comprehensive, flexible, and (usually) simple-to-understand service plans. CaaS service offerings are often bundled and may include integrated access to traditional voice (or VoIP) and data, advanced unified communications functionality such as video calling, web collaboration, chat, real-time presence and unified messaging, a handset, local and long-distance voice services, voice mail, advanced calling features (such as caller ID, three-way and conference calling, etc.)CaaS offers flexibility and scalability that small and medium-sized business might not otherwise be able to afford.
Cloud computing has evolved to include platforms for building and running custom web-based applications, a concept known as Platform-as-a-Service. PaaS is an outgrowth of the SaaS application delivery model. The PaaS model makes all of the facilities required to support the complete life cycle of building and delivering web applications and services entirely available from the Internet, all with no software downloads or installation for developers, IT managers, or end users. PaaS developers are concerned only with web-based development and generally do not care what operating system is used. PaaS services allow users to focus on innovation rather than complex infrastructure. Organizations can redirect a significant portion of their budgets to creating applications that provide real business value instead of worrying about all the infrastructure issues in a roll-your-own delivery model.
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) is the delivery of computer infrastructure (typically a platform virtualization environment) as a service. IaaS is centered around a model of service delivery that provisions a predefined, standardized infrastructure speci?cally optimized for the customer’s applications. IaaS providers manage the transition and hosting of selected applications on their infrastructure. Customers maintain ownership and management of their application(s) while off-loading hosting operations and infrastructure management to the IaaS provider. Provider-owned imple-
mentations typically include the following layered components:
- Computer hardware (typically set up as a grid for massive horizontal scalability)
- Computer network (including routers, firewalls, load balancing,etc.)
- Internet connectivity (often on OC 192 backbones )
- Platform virtualization environment for running client-specified virtual machines
- Service-level agreements
- Utility computing billing
Rather than purchasing data center space, servers, software, network equipment, etc., IaaS customers essentially rent those resources as a fully outsourced service. Usually, the service is billed on a monthly basis, just like a utility company bills customers. The customer is charged only for resources consumed.
A lot of IT organization can’t afford to invest in supercomputer-class infrastructure. Yet, the business could benefit from access to some pretty compute-intensive analytic applications. An interesting example of how one of these services might work is WolframAlpha, a query service based on a new model for doing sophisticated searches and calculations. WolframAlpha counts a company called Xignite, a provider of financial information via standard Web services protocols, as one of its partners. User of the WolframAlpha system are able to leverage the Xignite data alongside other data to query the WolframAlpha system about any calculation they can think of.
One of the advantages of cloud computing is that both small and medium sized businesses can instantly obtain the benefits of the enormous infrastructure without having to implement and administer it directly. This also permits accessibility to multiple data centers anywhere on the globe. It also means that as the need for resources increases, companies can add additional service as and when needed from the cloud computing vendor without having to pay for additional hardware.The other benefits are:
A low cost alternative to access technology:
With cloud computing coming into play, technology admission is no more a principal outlay. It more like how you utilize traditional utilities like electricity; pay for what you use and pay till you use it. This in order to enable companies to save their money on important business activities. Moreover it gives small and medium businesses an opportunity to access technology as a resource.
Optimum utilization and dispersion of cost:
While incorporating infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and software as a service (SaaS) cloud computing brings economies of costs and resources. Pooling of resources additionally guides to superior performance, load balancing (as the load capacity is centrally managed) and complete use of server capacity. In this way cloud computing results in enhanced resource consumption, which is exceptional from sustainability viewpoint.
Greater independence and remote access:
In cloud computing the infrastructure is maintained by a intermediary provider and accessed by customers by way of internet using web browser. In this way users can access the utility independent of place and infrastructure from a PC, laptop or a handheld device. This has also simplified the idea of offshore software development through the places offering relatively low cost IT outsourcing.
Enhanced monitoring and simplified usage:
On one hand where the model improve security and monitoring within a centralized data access, it simplifies usability by providing self service system interfaces on the other. The user need not be worried about back end engineering and parameters. Besides this, user does not need to install the application on his system, saving him from the trouble of software maintenance, ongoing operation, and support.
Monitoring benefits: central storage is easier to control and monitor. The flipside is the nightmare scenario of comprehensive data theft. However, I would rather spend my time as a security professional figuring out smart ways to protect and monitor access to data stored in one place (with the benefit of situational advantage) than trying to figure out all the places where the company data resides across a myriad of thick clients! You can get the benefits of Thin Clients today but Cloud Storage provides a way to centralise the data faster and potentially cheaper. The logistical challenge today is getting Terabytes of data to the Cloud in the first place.
Microsoft has introduced “The Azure Services Platform”, built from the ground up to be consistent with Microsoft’s commitment to openness and interoperability, promises to transform the way businesses operate and how consumers access their information and experience the Web. Most important, it gives our customers the power of choice to deploy applications in cloud-based Internet services or through on-premises servers, or to combine them in any way that makes the most sense for the needs of their business.
According to Microsoft the Azure Services Platform is an industry-leading move by Microsoft to help developers build the next generation of applications that will span from the cloud to the enterprise datacenter and deliver compelling new experiences across the PC, Web and phone.
The biggest challenges the companies face are secure data storage, high-speed access to the Internet, and standardization. Storing large amounts of data that is oriented around user privacy, identity, and application-specific preferences in centralized locations raises many concerns about data protection. These concerns, in turn, give rise to questions regarding the legal framework that should be implemented for a cloud-oriented environment. Another challenge to the cloud computing model is the fact that broadband
penetration in the United States remains far behind that of many other countries in Europe and Asia. Cloud computing is untenable without high-speed connections (both wired and wireless). Unless broadband speeds are available, cloud computing services cannot be made widely accessible.Finally, technical standards used for implementation of the various computer systems and applications necessary to make cloud computing work have still not been completely defined, publicly reviewed, and ratified by an oversight body. Even the consortiums that are forming need to get past that hurdle at some point, and until that happens, progress on new products will likely move at a snail’s pace.
The reliability of cloud computing has recently been a controversial topic in technology circles. Because of the public availability of a cloud environment, problems that occur in the cloud tend to receive lots of public exposure. Despite claims of reliablity, few cloud vendors have tight SLAs (service level agreements) that promise controlled downtime or offer rebates for excess downtime. Amazon goes the opposite direction and doesn’t offer any uptime guarantees, even cautioning users that their instance (or server) can disappear at any time and that they should plan accordingly. AppLogic-based clouds, provided by companies such as ENKI, are capable of offering better guarantees of uptime because of its inherent self-healing capabilities that can enable 3-4 nines of uptime.
Inorder to solve the various security issues and other challenges of cloud computing various research projects are being taken care of. Amidst the hype surrounding cloud computing, security issues are often raised, such as those involved with multiple customers having their data and applications sharing the same cloud resources. But researchers at the University of Washington also see lots of opportunity in the fact that Web services and applications will be so closely situated. CloudViews is a Hadoop HBase-supported common storage system being developed by the researchers “to facilitate collaboration through protected inter-service data sharing.” Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Software Systems have outlined a Trusted Cloud Computing Platform that “enables Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) providers such as Amazon EC2 to provide a closed box execution environment that guarantees confidential execution of guest virtual machines.” Such a platform would assure customers that service providers haven’t been messing with their data and would enable service providers to secure data even across many VMs. University of Maryland, Baltimore County researcher John Krautheim whose proposal is aimed at better sharing the risk responsibility between the cloud provider and customer, giving the customer much more control than is typically the case. “A method of combining the requirements of the user and provider is to let the clients control the security posture of their applications and virtual machines while letting the service provider control the security of the fabric. This provides a symbiotic security stance that can be very powerful provided both parties hold up their end of the agreement,”. Components of this approach will include having a method for shutting down VMs if necessary and monitoring/auditing from within and outside the PVI(Private Virtual Infrastructure).
Despite of all the challenges, cloud computing is emerging as a solution for many small to large organizations that cannot manage the storage of their data and cannot afford to have costly hardware and software for carrying out their work Like any evolving technology, cloud computing will see its fair share of growing pains. However, its one of those disruptive technologies that come once in a while that can radically change how we build, manage and consume software.
– Rohit Verma